
What is Digital Twin Technology?
The digital twin is the most effective physical device that provides a comprehensive view of its entire lifespan. Digital twins can simulate behavior and monitor physical activity by integrating real-time data collected by sensors and devices. Technology can transform many aspects of the real world, from individual consumer devices in businesses to large installations such as wind turbines and even entire districts in the city. With digital twins, you can monitor the performance of your assets, investigate potential problems, and make informed decisions about the maintenance and entire lifecycle of these assets.
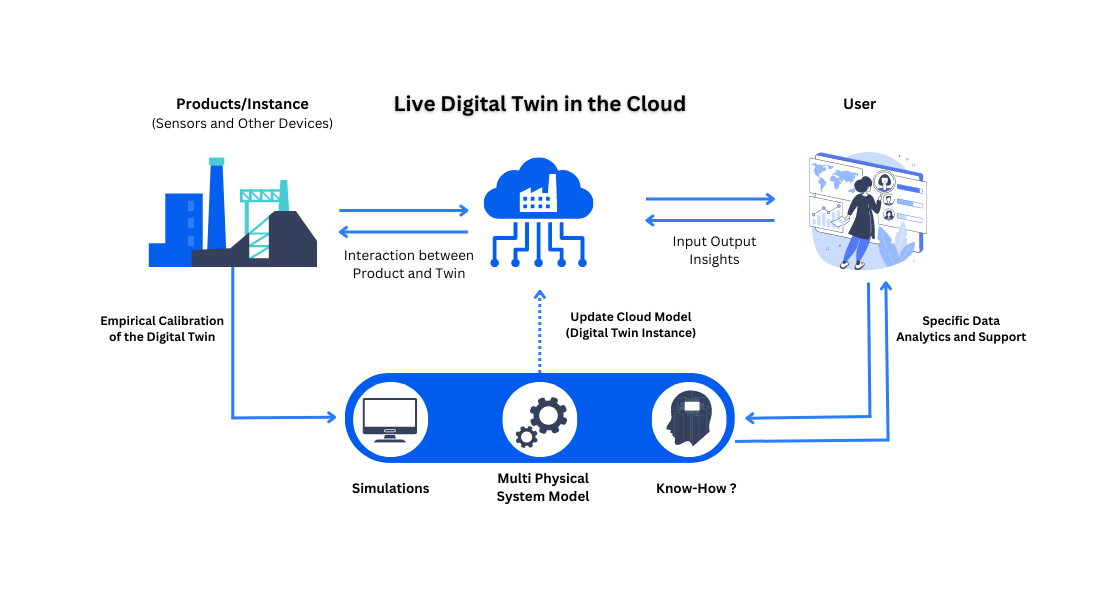
What Are the Benefits of Digital Twins?
1. Improved Performance
2. Predictive Capabilities
3. Remote Monitoring
Digital twins offer the advantage of remote monitoring and control of facilities, allowing for fewer personnel to physically inspect hazardous industrial equipment while ensuring effective oversight and safety.
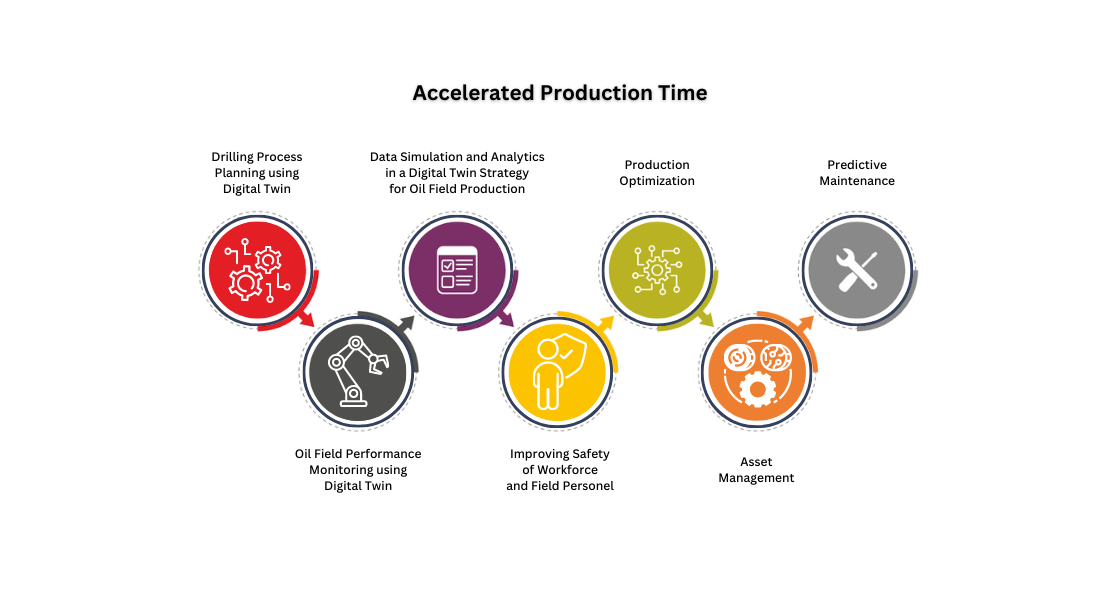
4. Accelerated Production Time
How Does A Digital Twin Work?
Digital twin technology functions by creating a virtual replica of a physical entity, encompassing its functions, properties, and behavior in a digital environment. By employing intelligent sensors that gather data from objects, real-time digital representations of assets can be generated. This powerful tool can be utilized throughout the entire life cycle of an asset, from initial product testing to its actual operation and eventual removal.
Digital twins incorporate various technologies to create a virtual representation of an asset, including the following.
1. Internet of Things
2. Artificial Intelligence
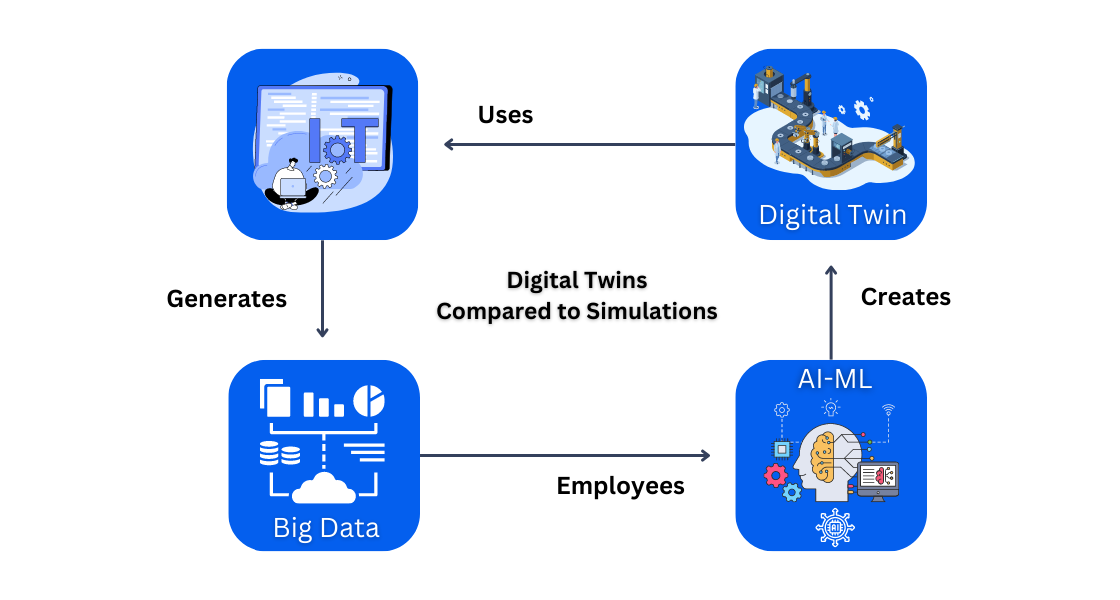
3. Digital Twins Compared to Simulations
A digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical asset that combines real-time information for maintenance and optimization. They focus on specific assets, provide high precision, and are used in industries such as manufacturing and healthcare. Simulation, on the other hand, creates computer models to study and predict behavior. They cover many systems, can be offline, and are based on mathematical models. Simulations are used in engineering, research, and education and have varying degrees of accuracy.
Types of Digital Twins
1. Component Twins/Parts Twins
2. Asset Twins
3. System or Unit Twins
4. Process Twins
Use Cases of Digital Twin Technology is in The Form of Assets Twin
1. Performance Optimization:
How Performance Optimization Can Be Used in the Form of a Digital Twin?
A. Real-Time Monitoring and Control:
B. Predictive Analytics:
C. Scenario Modeling:
D. Optimization Algorithms:
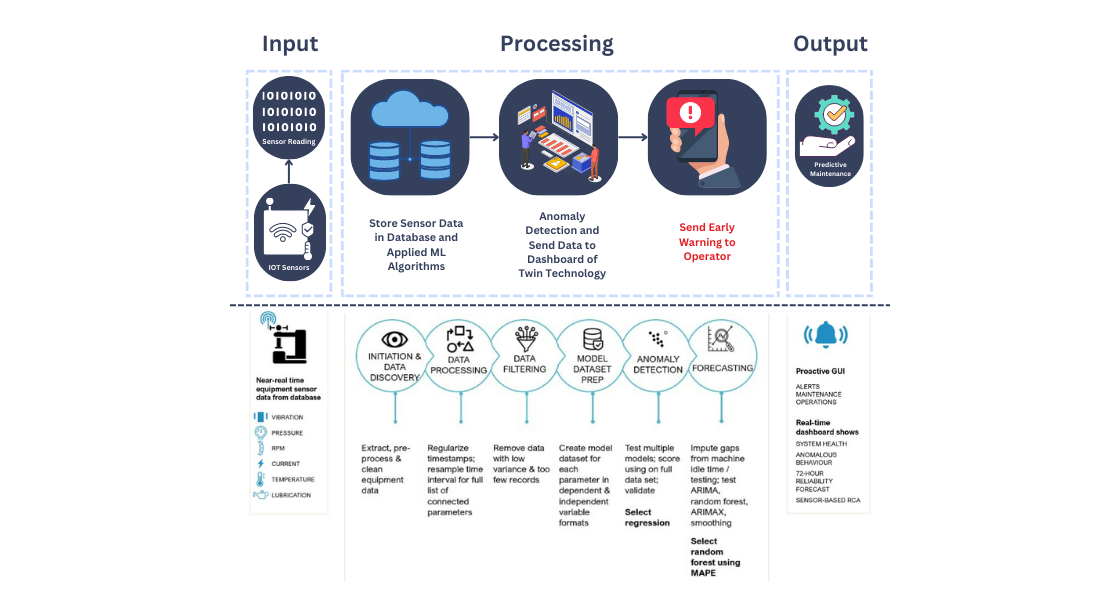
2. Predictive Maintenance:
How Predictive Maintenance Can Be Used in the Form of Digital Twin?
Predictive maintenance is one of the most common use cases for digital twins, and it involves using data from sensors and other sources to predict when maintenance should be performed on a physical asset. By monitoring the performance of a machine or piece of equipment in real-time, a digital twin can detect early signs of potential problems and alert operators before any issues occur. This can help prevent downtime, reduce maintenance costs, and improve overall equipment effectiveness.
Let’s consider an example of a wind turbine. A digital twin of a wind turbine can be created by integrating data from sensors that monitor the turbine’s performance, such as vibration sensors, temperature sensors, and pressure sensors. This data can be used to create a model of the turbine’s behavior, which can be used to predict when maintenance should be performed.
For instance, suppose that the digital twin detects an increase in vibration in the turbine’s gearbox. This could indicate that the gearbox is wearing out and will need to be replaced soon. The digital twin can alert operators to this issue, and maintenance can be scheduled to replace the gearbox before it fails. This can prevent costly downtime and reduce the risk of catastrophic failure.
The data from the digital twin can also be used to optimize maintenance schedules. For example, instead of performing maintenance on a fixed schedule, maintenance can be performed when it is actually needed, based on the data from the digital twin. This can reduce unnecessary maintenance and help operators prioritize maintenance tasks more effectively.
In addition to wind turbines, predictive maintenance with digital twins can be applied to other types of equipment, such as industrial pumps, HVAC systems, and manufacturing equipment. By using data to predict when maintenance is needed, digital twins can help improve equipment reliability and reduce maintenance costs.
3. Risk Management:
Asset twins can be used to simulate the impact of different scenarios on the performance of physical assets. This can help organizations identify risks and develop mitigation strategies.
4. Product Development:
Asset twins can be used to simulate the performance of physical assets during production. This can help organizations identify design issues and improve products before production.
Mr. Radhik Bhojani