Understand Parallel Programming
A computing concept known as parallel programming entails executing several operations concurrently as opposed to sequentially. Applications can complete tasks more quickly and effectively thanks to parallel programming, which makes use of multi-core processors
This is typically accomplished in C# parallel programming through the use of multithreading, parallel loops, and the Task Parallel Library (TPL.NET).
The Importance of Parallel Programming in Modern Applications
High-performance and responsive software is becoming more and more necessary in today’s software applications. Concurrent programming in C# is crucial for developers working on real-time, web, or data-intensive applications.
Nowadays, parallel programming is a crucial component of C# performance optimization, allowing programs to run workloads concurrently and maximize CPU utilization. Asynchronous programming in , Developers create applications that can grow in size and performance without being restricted by hardware limitations.
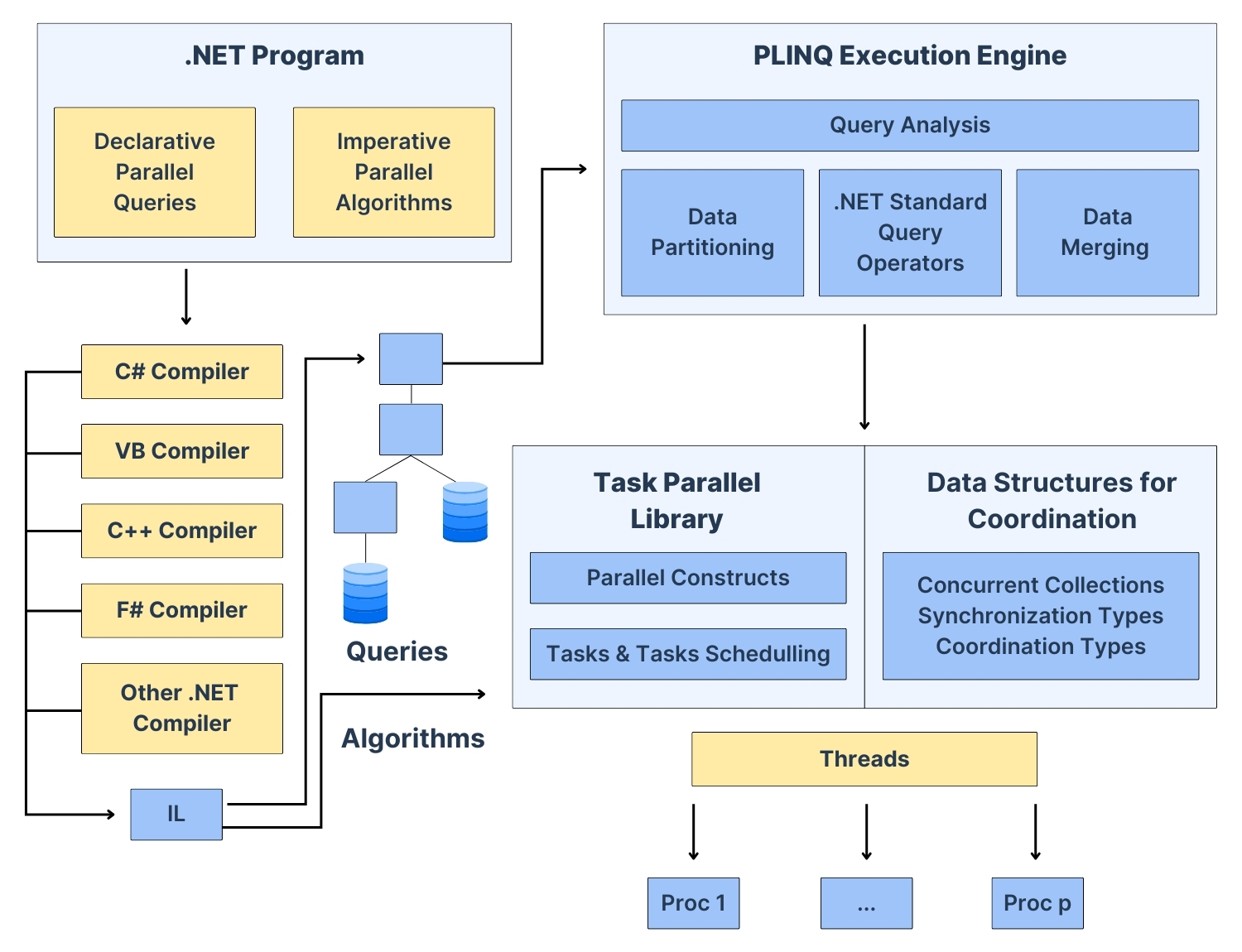
C# provides excellent support for parallel processing in .NET with the Task Parallel Library, PLINQ in C#, async-await, and concurrent collections in C#. In this blog post, we will discuss real-world use cases where parallel programming examples in C# can be applied. The above image is a parallelism example.
Learn more about our engineering capabilities.
1. CPU-Intensive Computations
Example: Parallelizing a Loop
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Parallel.For(0, 10, i =>
{
Console.WriteLine($"Processing {i} on thread {Task.CurrentId}");
});
}
}2. Web API Performance Improvement
Example: Fetching Data from Multiple APIs
using System;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
class Program
{
static async Task Main()
{
HttpClient client = new HttpClient();
Task<string> api1 = client.GetStringAsync("https://api.example.com/data1");
Task<string> api2 = client.GetStringAsync("https://api.example.com/data2");
await Task.WhenAll(api1, api2);
Console.WriteLine("Both API calls completed");
}
}3. Data Processing with PLINQ
Example: Parallel Processing of a Large Dataset
using System;
using System.Linq;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
var numbers = Enumerable.Range(1, 1000000);
var evenNumbers = numbers.AsParallel().Where(n => n % 2 == 0).ToList();
Console.WriteLine($"Found {evenNumbers.Count} even numbers");
}
}4. Real-Time Applications (Game Development, Stock Trading)
Example: Running Multiple Game Objects in Parallel
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
class Program
{
static async Task Main()
{
Task playerMovement = Task.Run(() => Console.WriteLine("Player Moving..."));
Task enemyAI = Task.Run(() => Console.WriteLine("Enemy AI Processing..."));
await Task.WhenAll(playerMovement, enemyAI);
}
}
5. Background Tasks in Desktop Applications
Example: Running a Background Task Without Freezing UI
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
public class MainForm : Form
{
private Button btnProcess;
public MainForm()
{
btnProcess = new Button { Text = "Start Process", Width = 150 };
btnProcess.Click += async (s, e) => await ProcessData();
Controls.Add(btnProcess);
}
private async Task ProcessData()
{
await Task.Run(() =>
{
// Simulating a long-running process
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(3000);
MessageBox.Show("Processing Complete");
});
}
}Looking to discuss your application requirements?
Conclusion
Parallel programming in C# is really useful because it helps make applications work better and faster. The Task Parallel Library and PLINQ and parallel loops and async-await in C# parallel programming lets developers make applications that can handle a lot of work and are very fast. C# parallel programming is a way to make applications that are scalable and have high performance. This is what makes C# parallel programming is so good, for making applications that need to do a lot of things at the time.
Knowledge of efficient thread-safe programming practices in C# and the ability to apply parallel programming concepts where necessary ensures optimal performance with minimal complexity. Parallel programming, when applied correctly, is a very effective technique in most real-world .NET applications.